- Overvew
- Table of Content
- Segmentation
- Segmentation
- Request Sample
Market Definition
Glycinates are chelated mineral compounds derived from the amino acid glycine. They enhance mineral absorption and bioavailability, making them widely used across food, nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, and animal feed industries. The market has evolved significantly due to rising health awareness, nutritional deficiencies, and growing demand for clean-label, highly bioavailable mineral supplements.
Market Insights
The global glycinates market has witnessed steady growth driven by increasing consumer focus on nutritional wellness and functional foods. Demand rebounded in 2023 after short-term supply disruptions caused by high raw material and energy prices in 2021–2022. Growth is being led by the dietary supplements and animal nutrition sectors, where mineral absorption efficiency is crucial. The shift toward sustainable and organic sources of nutrition, coupled with a preference for gentle-on-stomach formulations, has further propelled glycinates’ adoption.
The market outlook remains positive, with demand projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% between 2023 and 2030, supported by rising use in food fortification, personal care, and pharmaceutical formulations. However, fluctuating prices of key inputs such as glycine and metal salts (zinc, magnesium, calcium) continue to affect production costs. Supply concentration in China and East Asia also creates a degree of market vulnerability.
Regionally, Europe and North America dominate due to established nutraceutical industries and higher consumer awareness, while Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing market. Increasing urbanization, expanding middle-class income, and dietary diversification in countries such as India and China are creating new growth opportunities. Manufacturers are also focusing on product innovation, such as organic-certified and plant-based glycinates, to appeal to health-conscious consumers.
Market Dynamics: Drivers
The growing focus on nutritional efficiency, preventive healthcare, and animal feed optimization are key drivers. Glycinates are favored over inorganic mineral sources due to their high bioavailability, better digestive tolerance, and reduced environmental impact from excreted minerals. Rising investments in food fortification programs and dietary supplementation among aging populations are also supporting market expansion.
Market Dynamics: Challenges
Volatile raw material prices, particularly of glycine and metal salts, along with limited global suppliers, are constraining cost stability. Complex manufacturing processes and stringent food and pharma-grade regulations raise entry barriers for new players. Moreover, competition from other chelated minerals such as gluconates and citrates may limit penetration in certain segments.
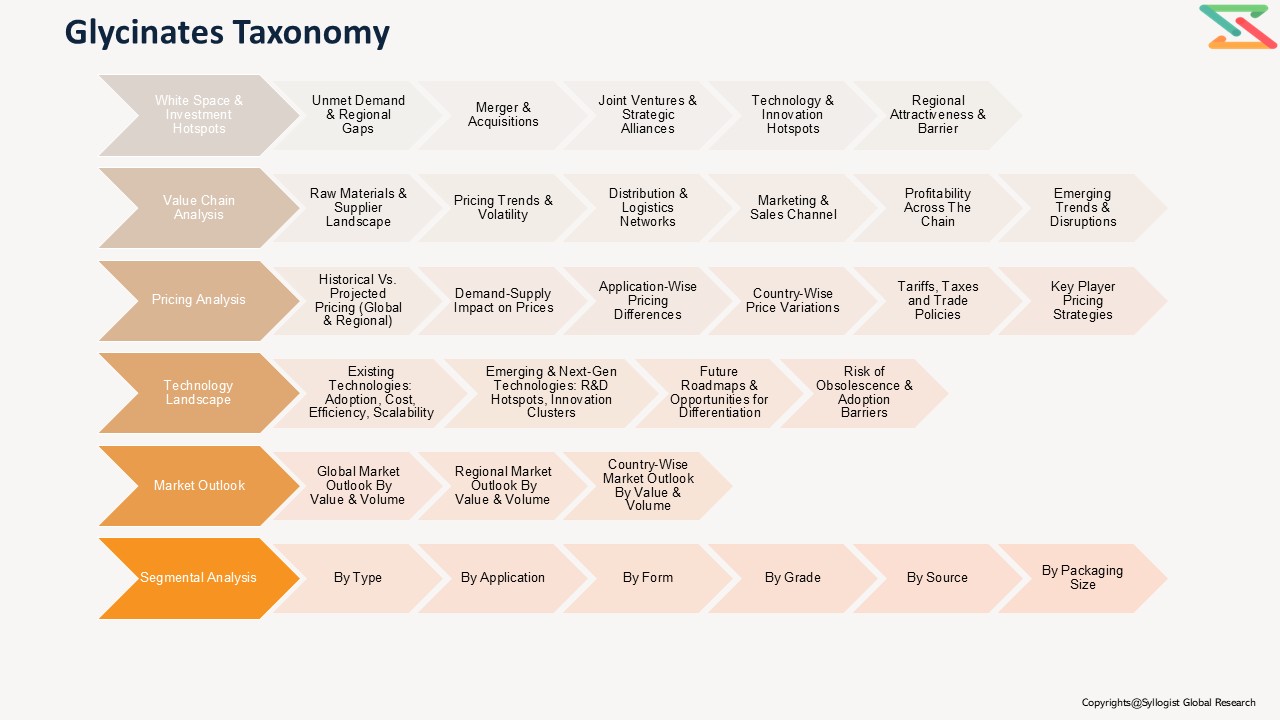
Market Segmentation
- Based on Type, the Global Glycinates Market is segmented into:
- Magnesium Glycinate
- Calcium Glycinate
- Zinc Glycinate
- Copper Glycinate
- Iron Glycinate
- Manganese Glycinate
- Sodium Glycinate
- Others
- Based on Application, the market is segmented into:
- Food & Beverages
- Dietary Supplements
- Pharmaceuticals
- Animal Feed
- Personal Care
- Others
- Based on Form, the market is segmented into:
- Dry
- Liquid
- Based on Region, the market is segmented into:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
All market revenues are presented in US Dollars; market volumes are expressed in tons.
Historical Year: 2021–2024
Base Year: 2025
Estimated Year: 2026
Forecast Period: 2027–2035
Key Questions this Study Will Answer
- What is the key overall market statistics and estimates (Market Size by Value & Volume, Forecast, Segmentation, and Market Shares) for the Global Glycinates Market?
- How do regional factors drive industry size, growth, and challenges across major markets?
- What are the latest innovations, opportunities, and trends shaping the Global Glycinates Market?
- Who are the major players, and how do they compare based on competitive benchmarking?
- What insights were derived from market surveys and primary discussions with industry participants?
- Market Foundations & Dynamics
- Introduction
1.1. Product Overview (Definition & Scope of Glycinates — metal glycinates, amino-acid chelates, glycine salts)
1.1.2. Chemical Lifecycle Overview (Synthesis → Purification → Formulation → End-use → Disposal/Recovery)
1.1.3. Research Methodology
1.1.4. Executive Summary
1.1.5. Major Trends Shaping the Market (clean-label, bioavailability focus, micronutrient deficiency remediation)
1.1.6. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Opportunities (feed & fertilizer demand vs. pharma & personal care uptake)
1.1.7. Comparison of Glycinates vs. Alternative Chelates (EDTA, amino-acid chelates, inorganic salts)
1.1.8. Scenario Planning (Base, Optimistic, Conservative)
1.1.9. Sensitivity Analysis (Raw material prices, regulatory shifts, crop cycles)
1.1.10. Identification of Regional Investment Hotspots - Market Dynamics
- Introduction
- Drivers (rising demand for bioavailable micronutrients, precision agriculture, regulatory moves away from synthetic chelants)
- Restraints (raw material volatility, technical barriers in scale-up, regulatory hurdles)
- Opportunities (specialty glycinates for pharma, nutraceuticals, fortified foods)
- Challenges (quality standards, supply chain traceability)
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- Market Ecosystem & Value Chain
3.1. Overview of Value Chain Participants
1.3.1.1. Raw Material Suppliers (glycine producers, mineral salts — zinc, magnesium, iron, manganese, copper)
1.3.1.2. Chemical Intermediate Manufacturers (chelation reactors, solvent & catalyst suppliers)
1.3.1.3. Manufactures / Formulators (powder, granule, liquid glycinates)
1.3.1.4. Specialty Additive Producers (feed premix, fertilizer blends, nutraceutical formulators)
1.3.1.5. Distribution & Trading Companies
1.3.1.6. End-Use Sectors (Agriculture, Animal Feed, Pharmaceuticals, Food & Beverage, Personal Care, Industrial)
1.3.2. Flow of Value and Material Through the Chain
1.3.3. Value Addition and Margins at Each Stage
1.3.3.1. Raw Material Procurement
1.3.3.2. Synthesis / Chelation / Reaction & Conversion
1.3.3.3. Purification & Drying / Crystallization
1.3.3.4. Formulation & Packaging
1.3.3.5. Distribution & Sales
1.3.4. Integration Trends (Manufacturer + Formulator vs. Specialist Suppliers)
1.3.5. Impact of Vertical Integration (control of glycine feedstock, captive mineral sourcing) - Mapping of Roles and Interdependencies
- Market Trends & Developments
5.1. White Market Space Analysis (unserved niches such as micro-nutrient foliar glycinates, pharma-grade glycinates)
1.5.2. Demand–Supply Gaps (glycine availability, high-purity grades)
1.5.3. Investment Hotspots (regions with strong agriculture modernization, nutraceutical growth)
1.5.4. Unmet Needs (standardized specifications, stable liquid formulations) - Risk Assessment Framework
6.1. Political / Geopolitical Risk (trade barriers on raw materials)
1.6.2. Operational Risk (process upsets, quality variation)
1.6.3. Environmental Risk (effluent, solvent handling)
1.6.4. Financial Risk (commodity price swings, currency exposure)
- Market Ecosystem & Value Chain
- Regulatory Framework & Standards
- Global Regulatory Overview
1.1. REACH and EU Chemical Regulations (registration, SVHC considerations)
2.1.2. U.S. FDA / EPA / TSCA implications for food, feed and industrial use
2.1.3. China chemical registration & food/feed additive rules
2.1.4. India FSSAI / AGMARK / feed additive regulations
2.2. Compliance & Certification Requirements (PhEur, USP for pharma grades; feed and fertilizer certifications)
2.3. Transportation and Storage Regulations (hazard classification, shipping of mineral salts & concentrated liquids)
2.4. Safety & Quality Standards (impurity limits, heavy metal thresholds, microbiological standards for food/feed grades)
2.5. Environmental & Liability Considerations (wastewater, worker safety)
2.6. Traceability & Digital Documentation (supply chain traceability, certificates of analysis)
- Global Regulatory Overview
- Technology Landscape
- Synthesis & Chelation Technologies
1.1. Direct Salt Formation (acid-base neutralization routes)
3.1.2. Advanced Chelation Methods (controlled pH, ligand excess, solvent systems)
3.2. Purification & Crystallization Techniques (spray drying, crystallizers, filtration)
3.3. Formulation Technologies (dry blends, granules, aqueous solutions, microencapsulation)
3.4. Quality Control & Analytical Methods (HPLC, IC, ICP-MS for metal content, moisture analysis)
3.5. Process Intensification & Continuous Manufacturing Opportunities
3.6. Innovations to Reduce Cost & Improve Bioavailability (nano-formulations, coated granules)
3.7. Packaging & Stability Technologies (to prevent hygroscopicity, oxidative degradation)
- Synthesis & Chelation Technologies
- Global, Regional & Country Forecasts (2020–2035)
- Global Glycinates Market Outlook (value, volume)
- Market Share by:
2.1. By Application/End-Use (Agriculture — foliar & soil, Animal Feed, Human Nutrition & Nutraceuticals, Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care, Industrial)
4.2.2. By Product Type (Zinc Glycinate, Magnesium Glycinate, Iron Glycinate, Copper Glycinate, Calcium Glycinate, Others)
4.2.3. By Form (Powder/Granule, Liquid, Stabilized/Coated)
4.2.4. By Purity Grade (Technical, Feed Grade, Food/Nutraceutical Grade, Pharmaceutical Grade)
4.2.5. By Source (Bulk chemical manufacturers, specialty chelate producers)
4.2.6. By Packaging Size (Bulk, Bagged, IBC, Retail)
4.2.7. By Company - Regional & Country Outlook (2020–2035)
3.1. Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Australia)
4.3.2. North America (U.S., Canada, Mexico)
4.3.3. Europe (Germany, UK, Netherlands, France)
4.3.4. Latin America (Brazil, Argentina)
4.3.5. Middle East & Africa (UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa)
- Pricing Analysis
- Overview of Pricing Structures (per kg / per ton / price by purity grade)
2. Average Selling Price (ASP) Trends by Product Type and Region
5.3. Cost Benchmark:
5.3.1. Glycinate vs. Inorganic Salt Alternatives (e.g., zinc sulfate)
5.3.2. Cost per Effective Bioavailable Unit (value proposition)
5.4. Price Sensitivity by Application (fertilizer blends vs. pharma)
5.5. Historical Price Evolution (2015–2025)
5.6. Forecast Pricing Curve (2025–2035)
5.7. Factors Influencing Price:
5.7.1. Glycine Feedstock Price & Availability
5.7.2. Mineral Salt Prices (Zn, Mg, Fe, Cu)
5.7.3. Energy, Utilities, and Logistics
5.7.4. Purification & Certification Costs
5.8. Regional Pricing Differentiation (Asia vs. Europe vs. North America)
5.9. Impact of Raw Material Cost Fluctuations on Glycinate Pricing
- Overview of Pricing Structures (per kg / per ton / price by purity grade)
- Competition Outlook
- Market Concentration and Fragmentation Level
2. Company Market Shares (Top 10 Players — global & regional leaders)
6.3. Competitive Strategies (vertical integration, specialty grades, formulation partnerships)
6.4. Benchmarking Matrix (Product Range vs. Purity vs. Geographic Reach)
6.5. Recent Developments (M&A, capacity expansions, joint ventures, new product launches)
- Market Concentration and Fragmentation Level
- Cost Structure & Margin Analysis
- Detailed Cost Breakdown (glycine procurement, mineral salts, utilities, chemicals, labor)
2. Average Cost per Stage (synthesis, purification, formulation, packaging)
7.3. Profitability and Margin Distribution Along Value Chain
7.3.1. Raw Material Supplier Margin
7.3.2. Glycinate Manufacturer Margin
7.3.3. Formulator / Premix Manufacturer Margin
7.3.4. Distributor / Trader Margin
7.4. Sensitivity Analysis: How Raw Material Prices & Purity Requirements Impact Margin
7.5. Cost Reduction Opportunities (process optimization, backward integration, co-location with glycine producers)
- Detailed Cost Breakdown (glycine procurement, mineral salts, utilities, chemicals, labor)
- Business Models & Strategic Insights
- Bulk Commodity Supplier Models
2. Specialty & High-Purity Producer Models (pharma & nutraceutical focus)
8.3. Formulator & Value-Added Blends (fertilizer & feed premixes)
8.4. Contract Manufacturing & Toll Processing Models
8.5. Integrated Supply (from glycine feedstock to finished product)
8.6. Economic Viability Comparison of Models
8.7. SWOT Analysis of Leading Models
- Bulk Commodity Supplier Models
- Investment & Financial Analysis
- CAPEX and OPEX Benchmarks for Glycinate Manufacturing Plants (small, medium, large scale)
2. Payback Period and IRR Sensitivity (by region & product mix)
9.3. Financial Modeling Assumptions (capacity utilization, yield, price realizations)
9.4. Revenue Streams:
9.4.1. Bulk & Industrial Sales
9.4.2. Premium Food/Pharma Grade Sales
9.4.3. Formulated Product Sales (premixes, fertilizers)
9.4.4. Toll Manufacturing / Contract R&D
9.5. Investment Case Studies (greenfield plant, capacity expansion, backward integration)
9.6. Funding Landscape: Strategic Investors, Private Equity, R&D Grants
- CAPEX and OPEX Benchmarks for Glycinate Manufacturing Plants (small, medium, large scale)
- Sales & Distribution Channel Analysis
- Overview of Go-to-Market Channels
1.1. Direct Sales (manufacturer → large end-user)
10.1.2. Indirect Sales via Distributors & Traders
10.1.3. E-commerce & Small-pack Retail Channels (nutraceuticals, personal care)
10.2. Channel Share by Region
10.3. Typical Channel Flow Diagram (manufacture → formulation → distribution → end-use)
10.4. Sales Process (order sizing, QC, certification, logistics)
10.5. Distribution Strategies by Leading Players (local warehouses, captive logistics)
10.6. Emerging Trends:
10.6.1. On-demand Toll Manufacturing Platforms
10.6.2. Direct B2B Marketplaces for Specialty Chemicals
10.6.3. Co-branding / Co-formulation Partnerships
- Overview of Go-to-Market Channels
- Strategic Recommendations & Roadmap
- Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives (product diversification, geographic expansion)
2. Future Outlook (next 5–10 years — premiumization, regulatory tightening, sustainability)
11.3. Strategic Recommendations
11.3.1. Technology & Process Advancements to Watch (continuous chelation, greener solvents)
11.3.2. Circularity & Raw Material Security Roadmap (2030–2035)
11.3.3. Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders (manufacturers, formulators, investors)
11.4. Glycinates Market Acceleration Roadmap
11.4.1. Short-term (2025–2027): Quality standardization, targeted R&D, pilot formulations
11.4.2. Mid-term (2028–2030): Scale-up of specialty grades, backward integration, geographic hubs
11.4.3. Long-term (2031–2035): Sustainable feedstock sourcing, high-value pharma & nutraceutical penetration
11.5. Tailored recommendations for:
11.5.1. Glycinate Manufacturers
11.5.2. Formulators / Premix Producers
11.5.3. End Users (agri-input companies, feed houses, nutraceutical brands)
11.6. Recommendations on Key Success Factors
11.6.1. Strategic Partnerships & Alliances (raw material, formulation, distribution)
11.6.2. Digitalization & Quality Traceability (blockchain COAs, digital QC dashboards)
11.6.3. Regulatory Alignment & Certification Compliance
11.6.4. Investor Confidence & Capital Availability
- Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives (product diversification, geographic expansion)