- Overvew
- Table of Content
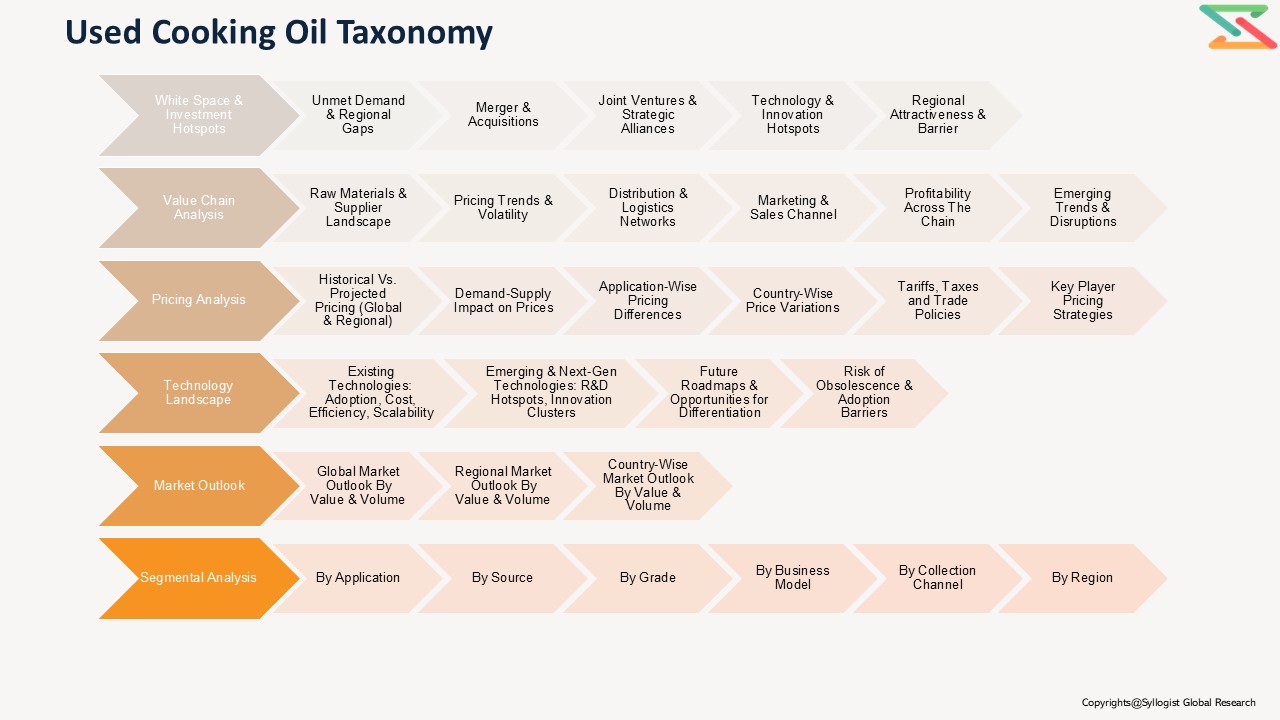
- Segmentation
- Request Sample
Market Definition
Used Cooking Oil (UCO) refers to vegetable oil or animal fat that has been utilized for cooking or frying purposes and is no longer fit for human consumption due to alterations in its chemical composition and physical properties caused by repeated heating. It primarily includes waste oils generated from household kitchens, restaurants, hotels, food processing industries, and catering services. UCO is an increasingly valuable resource as it can be collected and refined for use in biodiesel production, animal feed, oleochemicals, and other industrial applications. Growing environmental awareness and the need to reduce dependence on fossil fuels have brought UCO into focus as a key component of the circular economy.
Market Insights
The global used cooking oil market is witnessing significant transformation driven by sustainability mandates, renewable energy policies, and advancements in waste oil collection and refining technologies. The market was valued at approximately USD 7.9 billion in 2023 and is expected to reach around USD 12.4 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of about 6.5% during the forecast period. Increasing biodiesel production across Europe and North America remains the primary demand driver, as UCO serves as an essential feedstock for second-generation biofuels under mandates such as the EU Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) and the U.S. Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS). Several countries, including the UK, Germany, Spain, and the Netherlands, have established structured collection networks and trading platforms to encourage sustainable UCO recovery and reuse.
However, regional collection efficiency and feedstock availability vary widely. Europe remains the largest UCO producer and consumer due to its stringent sustainability goals and robust biodiesel blending targets. Asia-Pacific, led by China and India, is expected to record the fastest growth during the forecast period due to expanding food service sectors, rising environmental awareness, and supportive waste management policies. Nonetheless, lack of standardized collection infrastructure and prevalence of informal collection channels pose challenges to feedstock traceability and quality assurance in developing markets. Additionally, UCO prices are volatile, influenced by seasonal consumption patterns, food service output, and biodiesel market dynamics.
The UCO market is also benefiting from a rising focus on circular economy models and waste-to-value initiatives. Growing awareness regarding the negative environmental impact of improper oil disposal, such as clogged drainage systems, water pollution, and methane emissions, has accelerated the enforcement of waste oil collection regulations. Technological advancements in UCO filtration and pre-treatment are further enhancing conversion efficiency, thereby making UCO-based biofuels more economically viable. Strategic collaborations between restaurant chains, biodiesel producers, and waste management firms are strengthening collection networks and improving supply chain traceability. Moreover, policy incentives and tax benefits for renewable fuel producers are likely to further propel market expansion in the coming years.
Market Dynamics: Drivers
The increasing global emphasis on renewable energy and sustainable waste management is a key driver for the used cooking oil market. Governments and regulatory bodies are promoting the use of advanced biofuels as part of their carbon reduction commitments, creating strong demand for waste-based feedstocks. UCO-derived biodiesel reduces greenhouse gas emissions by up to 80% compared to fossil diesel. Additionally, expanding food service industries in emerging economies are generating large quantities of recoverable UCO. Rising environmental awareness among food businesses and households regarding proper oil disposal, combined with the potential for monetization through organized collection systems, is boosting supply availability. The alignment of circular economy objectives with waste valorization strategies further enhances the market’s long-term growth potential.
Market Dynamics: Challenges
Despite its potential, the UCO market faces several operational and regulatory challenges. Informal and unregulated collection practices in many regions result in inconsistent feedstock quality and traceability issues, posing risks to biodiesel producers who must meet sustainability certification requirements. The reuse of UCO for cooking in certain low-income regions continues to be a concern, both for public health and environmental reasons. High logistics costs, inadequate collection infrastructure, and contamination during storage and transportation also hinder efficient market operations. Furthermore, competition for feedstock from other industries such as oleochemicals and animal feed manufacturing may exert upward pressure on UCO prices. Addressing these challenges will require stricter policy enforcement, better public awareness, and investment in advanced collection and processing technologies.
Market Segmentation
- By Source:
- Household Sector
- Food Service Sector (Restaurants, Hotels, Caterers, Institutional Kitchens)
- Food Processing Industry
- By Application:
- Biodiesel Production
- Animal Feed
- Oleochemicals (Soaps, Detergents, Lubricants, Surfactants)
- Industrial Applications (Resins, Waxes, Lubricants)
- By End User:
- Biofuel Producers
- Chemical Manufacturers
- Feed Producers
- Waste Management Companies
- By Collection Method:
- Organized Collection Networks
- Informal/Unregulated Collection
- By Geography:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
All market revenues are expressed in USD, and market volumes are measured in million liters.
Historical Year: 2021–2024 | Base Year: 2025 | Estimated Year: 2026 | Forecast Period: 2027–2031
Key Questions this Study Will Answer
- What are the key market statistics (market size by value and volume, forecast numbers, and market segmentation) for the Global Used Cooking Oil Market?
- Which regions and applications are driving the highest demand growth, and what are their key regulatory and economic drivers?
- What innovations, policy frameworks, and technological developments are shaping the UCO market?
- Who are the leading competitors, and how do their business models and sourcing networks compare in terms of efficiency and compliance?
- What are the key findings from industry surveys and stakeholder interviews conducted during the study, and how do they inform future market opportunities?
- Market Foundations & Dynamics
- Introduction
1.1. Product Overview (Definition & Scope of Used Cooking Oil)
1.1.2. UCO Value Chain Overview (Collection → Aggregation → Processing → Conversion → End-Use)
1.1.3. Research Methodology
1.1.4. Executive Summary
1.1.5. Major Trends Shaping the Market (Biofuels, Circular Economy, Food Waste Regulation)
1.1.6. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Opportunities
1.1.7. Comparison of UCO Utilization Pathways (Biodiesel vs. Renewable Diesel vs. Oleochemicals)
1.1.8. Scenario Planning (Base, Optimistic, Conservative)
1.1.9. Sensitivity Analysis (Feedstock Availability, Oil Price, Policy Support)
1.1.10. Identification of Regional Investment Hotspots - Market Dynamics
- Introduction
- Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, and Challenges
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- Market Ecosystem & Value Chain
3.1. Overview of Value Chain Participants
1.3.1.1. Food Service Providers (Hotels, Restaurants, QSR Chains)
1.3.1.2. Collection & Aggregation Companies
1.3.1.3. Processing / Refining Firms
1.3.1.4. Biofuel Producers (Biodiesel & HVO Plants)
1.3.1.5. Traders & Exporters
1.3.1.6. End-Use Sectors (Transportation, Industrial, Energy)
1.3.2. Flow of Value and Material Through the Chain
1.3.3. Value Addition and Margins at Each Stage
1.3.3.1. Collection
1.3.3.2. Pre-Treatment / Filtering
1.3.3.3. Conversion (Esterification / Hydrogenation)
1.3.3.4. Distribution
1.3.4. Integration Trends (Vertically Integrated Biofuel Producers vs. Independent Collectors)
1.3.5. Impact of Vertical Integration - Mapping of Roles and Interdependencies
- Market Trends & Developments
5.1. White Market Space Analysis (Illegal UCO Trade, Informal Sector)
1.5.2. Demand–Supply Gaps
1.5.3. Investment Hotspots
1.5.4. Unmet Needs - Risk Assessment Framework
6.1. Political / Geopolitical Risk
1.6.2. Operational Risk (Collection Efficiency, Quality Variability)
1.6.3. Environmental Risk (Contamination, Disposal)
1.6.4. Financial Risk (Price Volatility, Policy Dependency)
- Market Ecosystem & Value Chain
- Regulatory Framework & Standards
- Global Regulatory Overview
1.1. EU Renewable Energy Directive (RED II & RED III)
2.1.2. U.S. EPA & LCFS Policies (RFS, California LCFS)
2.1.3. China’s Waste Oil Utilization Policy
2.1.4. India’s Biofuel Policy & FSSAI UCO Guidelines - Collection, Transportation & Storage Regulations
3. Export/Import Policies (EU–Asia Trade Corridors)
2.4. Sustainability & Traceability Standards (ISCC, RSPO, RSB)
2.5. Environmental & Liability Considerations
2.6. Digital Traceability & Certification Initiatives
- Global Regulatory Overview
- Technology Landscape
- UCO Collection & Filtration Technologies
2. Conversion Technologies
3.2.1. Transesterification for Biodiesel
3.2.2. Hydroprocessing for Renewable Diesel (HVO)
3.3. Pre-Treatment Innovations (Dehydration, Degumming, Acid Esterification)
3.4. Quality Control & Testing (FFA, Moisture, Impurities)
3.5. Digitalization & IoT in Collection Networks
3.6. Future Outlook: Algae & Synthetic Fuel Integration
- UCO Collection & Filtration Technologies
- Global, Regional & Country Forecasts (2020–2035)
- Global Used Cooking Oil Market Outlook (Volume & Value)
2. Market Share by:
4.2.1. Application (Biodiesel, Renewable Diesel, Animal Feed, Oleochemicals, Other Industrial Uses)
4.2.2. Source (Household, Restaurants, Food Processing Industries)
4.2.3. Quality Grade (High-Grade, Low-Grade, Mixed Feedstock)
4.2.4. Collection Channel (Formal, Informal, Integrated)
4.2.5. Business Model (Direct Collection, Aggregator Model, Franchise / Contract-Based Model)
4.3. Regional & Country Outlook (2020–2035)
4.3.1. Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain)
4.3.2. Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Indonesia)
4.3.3. North America (U.S., Canada)
4.3.4. Latin America (Brazil, Mexico)
4.3.5. Middle East & Africa (UAE, South Africa, Saudi Arabia)
- Global Used Cooking Oil Market Outlook (Volume & Value)
- Pricing Analysis
- Overview of Pricing Structures (per MT / per liter basis)
2. Average Selling Price (ASP) Trends by Region and Quality
5.3. Cost Benchmark:
5.3.1. Virgin Oil vs. UCO Feedstock for Biofuel
5.3.2. Renewable Diesel vs. Biodiesel Feedstock Cost Comparison
5.4. Price Sensitivity by Application (Biodiesel, Oleochemicals)
5.5. Historical Price Evolution (2015–2025)
5.6. Forecast Pricing Curve (2025–2035)
5.7. Factors Influencing Price:
5.7.1. Feedstock Availability
5.7.2. Logistics & Collection Cost
5.7.3. Quality Variability
5.7.4. Policy Incentives / Subsidies
5.8. Regional Pricing Differentiation (EU vs. Asia vs. U.S.)
5.9. Impact of Biofuel Policy Changes on UCO Pricing
- Overview of Pricing Structures (per MT / per liter basis)
- Competition Outlook
- Market Concentration and Fragmentation Level
2. Company Market Shares (Top 10 Players)
6.3. Competitive Strategies
6.3.1. Vertical Integration (Collection to Conversion)
6.3.2. Joint Ventures & Strategic Partnerships
6.3.3. Long-Term Supply Contracts with Biofuel Producers
6.4. Benchmarking Matrix (Scale vs. Integration vs. Feedstock Security)
6.5. Recent Developments (Partnerships, M&A, Capacity Expansions)
- Market Concentration and Fragmentation Level
- Cost Structure & Margin Analysis
- Detailed Cost Breakdown
1.1. Collection & Transportation
7.1.2. Storage & Pre-Treatment
7.1.3. Processing / Conversion
7.1.4. Quality Testing & Certification
7.1.5. Logistics / Export
7.2. Average Cost per Stage ($/MT)
7.3. Profitability and Margin Distribution Along the Value Chain
7.3.1. Collector Margin
7.3.2. Aggregator Margin
7.3.3. Processor / Converter Margin
7.3.4. Distributor Margin
7.4. Sensitivity Analysis: Oil Price & Feedstock Quality Impact on Margin
7.5. Cost Reduction Opportunities via Automation & Route Optimization
- Detailed Cost Breakdown
- Business Models & Strategic Insights
- Integrated Collection-to-Conversion Models
2. Independent Collector Networks
8.3. Franchise / Contracted Collection Models
8.4. UCO Trading & Export-Oriented Models
8.5. Partnerships with Biofuel Producers / Refineries
8.6. Economic Viability Comparison of Models
8.7. SWOT Analysis of Leading Business Models
- Integrated Collection-to-Conversion Models
- Investment & Financial Analysis
- CAPEX and OPEX Benchmarks for UCO Collection & Processing Units
2. Payback Period and IRR Sensitivity (by Application)
9.3. Financial Modeling Assumptions (Feedstock Price, Yield, Conversion Cost)
9.4. Revenue Streams:
9.4.1. Feedstock Sales to Biodiesel Producers
9.4.2. Renewable Fuel Credits / Carbon Credits
9.4.3. Byproduct Sales (Glycerin, Soap Base, etc.)
9.5. Investment Case Studies
9.6. Funding Landscape (Private Equity, ESG Funds, Circular Economy Initiatives)
- CAPEX and OPEX Benchmarks for UCO Collection & Processing Units
- Sales & Distribution Channel Analysis
- Overview of Go-to-Market Channels
1.1. Direct Sales (Collectors to Refineries)
10.1.2. Indirect Sales via Traders / Aggregators
10.1.3. Partnership Models (Restaurant Chains + Biofuel Producers)
10.1.4. Online Platforms for Waste Oil Trading
10.2. Channel Share by Region
10.3. Typical Channel Flow Diagram
10.4. Sales Process (Collection → Aggregation → Processing → Conversion → Export)
10.5. Distribution Strategies by Leading Players
10.6. Emerging Trends:
10.6.1. Platformization / Digital Marketplaces
10.6.2. Circular Supply Chain Partnerships
10.6.3. Traceable & Certified UCO Supply Models
- Overview of Go-to-Market Channels
- Strategic Recommendations & Roadmap
- Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives
2. Future Outlook (2025–2035, Emerging Players & Success Factors)
11.3. Strategic Recommendations
11.3.1. Technology Advancements to Watch
11.3.2. Circular Economy Integration Roadmap (2030–2035)
11.3.3. Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
11.4. Used Cooking Oil Market Acceleration Roadmap
11.4.1. Short-Term (2025–2027)
11.4.2. Mid-Term (2028–2030)
11.4.3. Long-Term (2031–2035)
11.5. Tailored Recommendations for:
11.5.1. UCO Collectors & Aggregators
11.5.2. Biofuel Producers
11.5.3. Policymakers & Regulators
11.5.4. Investors & Financial Institutions
11.6. Recommendations on Key Success Factors
11.6.1. Partnerships & Traceable Networks
11.6.2. Digitalization & Efficiency Optimization
11.6.3. Policy Alignment & Certification Compliance
11.6.4. Investor Confidence & Sustainable Capital Access
- Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives