- Overvew
- Table of Content
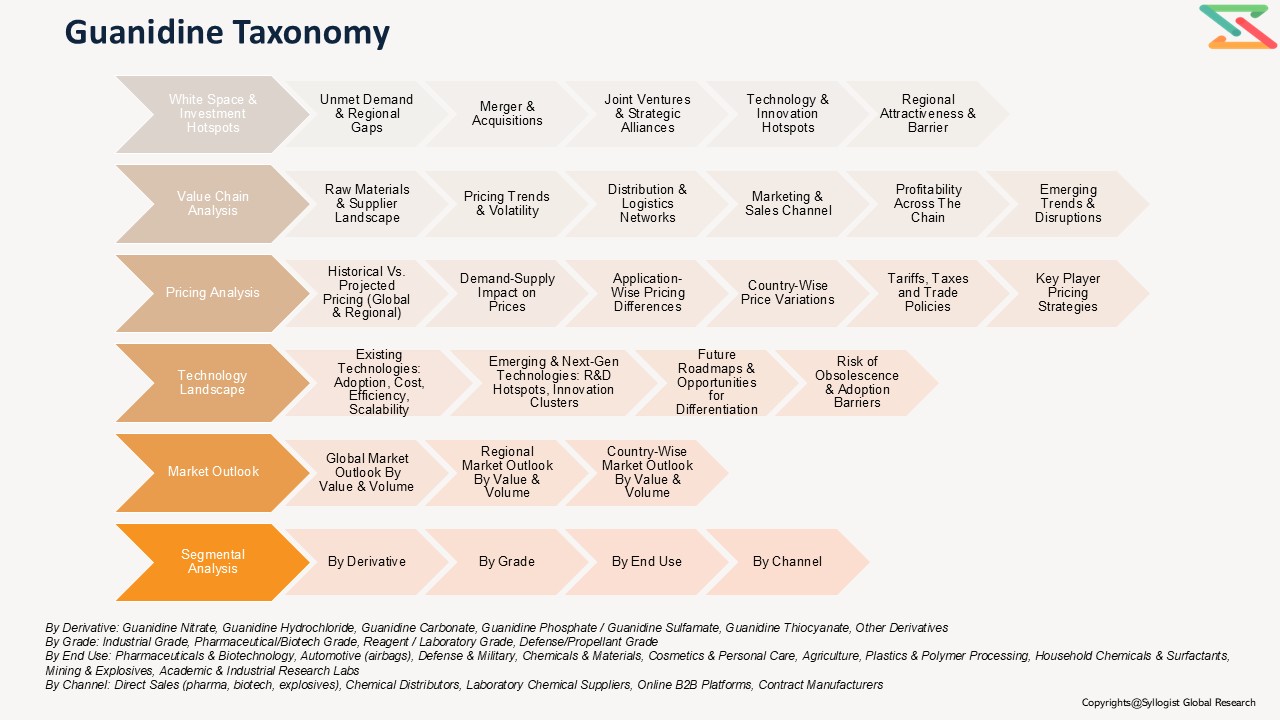
- Segmentation
- Segmentation
- Request Sample
Global Guanidine Market: Strategic Intermediate Powering High-Value Chemical Synthesis
Driving Industrial Transformation Through Application-Specific Innovation
The global guanidine market is entering a phase of accelerated advancement, driven by improvements in synthesis efficiency, purity enhancement technologies, and expanding adoption across pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, electronics, and specialty materials. Guanidine and its derivatives, such as guanidine nitrate, guanidine carbonate, guanidine hydrochloride, and biguanides, are critical building blocks in API manufacturing, high-energy materials, polymer additives, disinfectants, and advanced catalysts. Innovation is increasingly centered on achieving higher purity grades, safer handling characteristics, improved stability, and environmentally aligned production routes. Regulatory tightening in pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals (US FDA, EMA, REACH) is reshaping industry standards toward ultra-low impurity guanidine intermediates with higher consistency and traceability. In parallel, advances in catalytic synthesis, continuous processing, and green ammonia/urea routes are improving yields and reducing energy intensity. These developments reflect a strategic modernization of the global guanidine industry, positioning it as an essential enabler of next-generation drug development, crop protection, and high-performance materials.
Mapping the Value Chain: From Urea & Ammonia to High-Value Guanidine Derivatives
The guanidine value chain is tightly linked to upstream availability of urea, ammonia, hydrogen cyanide (HCN), and formamide, key precursors that directly determine cost competitiveness and production stability. Guanidine is primarily synthesized via urea-based or cyanamide-based processes, where catalyst selection, temperature control, and continuous reaction optimization play decisive roles in quality and yield. Midstream, producers convert guanidine into a broad range of derivatives including guanidine hydrochloride, guanidine nitrate, guanidine carbonate, dicyandiamide (DCD), biguanides (e.g., PHMB), and specialty salts used for pharmaceuticals and polymer chemistry. These derivatives are integral to industries such as API synthesis, crop protection formulations, explosives, personal care preservatives, water treatment, flame retardants, and epoxy resin curing systems.
Downstream demand is primarily driven by pharmaceutical intermediates, where guanidine-based building blocks are used in cardiovascular, antiviral, and CNS drugs. Agrochemical applications (herbicides, pesticides, nitrification inhibitors) form another significant demand pillar, particularly in rapidly growing agricultural economies. Electronics and resin additives further reinforce demand for high-purity guanidine salts. Increasingly stringent regulatory requirements in pharma and agrochemicals are pushing producers toward backward integration (formamide/HCN/urea) and forward integration into specialty formulations to ensure supply security, traceability, and customer proximity.
Balancing Global Demand and Supply Dynamics
Global demand for guanidine exhibits stable structural growth, supported by long-term trends in API manufacturing, agricultural productivity enhancement, and expansion of high-performance materials. Asia Pacific, especially China and India, continues to lead consumption and production due to strong pharmaceutical and agrochemical manufacturing ecosystems. Europe maintains significant demand for high-purity grades used in regulated pharma and specialty chemical applications, while North America shows steady demand for guanidine derivatives used in industrial resins, healthcare, and electronics.
Supply-side dynamics remain sensitive to raw material costs, particularly urea, formamide, ammonia, and HCN, along with energy-intensive process requirements and environmental compliance obligations. Restrictions on cyanide handling, hazardous waste disposal, and emission norms are increasing production costs in Western markets, gradually shifting capacity expansion toward Asia and parts of the Middle East. However, stringent pharmaceutical-grade specifications and qualification cycles limit the ability of new entrants to rapidly penetrate high-value segments. These structural factors underscore the need for capacity planning, backward integration, robust raw material security, and regional diversification across the guanidine value chain.
Pricing Dynamics: Navigating Feedstock Sensitivity and Regulatory Pressures
Pricing in the guanidine market is heavily influenced by fluctuations in upstream feedstocks, most notably urea, ammonia, and energy costs, along with environmental compliance investments associated with handling toxic intermediates such as cyanamide and HCN. Regions with lower-cost urea and energy (China, Middle East) maintain competitive pricing structures, while Europe and North America typically exhibit significant premiums for GMP-grade, pharma-grade, and specialized high-purity guanidine salts. Specialty derivatives including guanidine nitrate (for energetic materials), guanidine hydrochloride (for APIs and protein denaturation), and biguanides (for personal care and disinfection) command substantial price variations based on purity, stabilization, and end-use criticality.
Regulatory developments, especially around pharmaceutical quality norms, antimicrobial usage restrictions, and environmental controls on nitrogen compounds, are shaping cost structures and influencing product differentiation. As global demand shifts toward safer, cleaner, and more consistent guanidine intermediates, producers are increasingly emphasizing value delivery through higher purity, impurity profiling, precise particle-size control, and secure supply chains rather than price competition alone.
White Space and Emerging Investment Hotspots
The guanidine market presents substantial white-space opportunities driven by innovations in pharmaceuticals, agriculture, energy materials, and specialty polymers. Rising R&D investment in cardiovascular and CNS drugs is expanding demand for guanidine-based intermediates in API synthesis. Agrochemical producers are increasingly adopting guanidine derivatives such as DCD and biguanides for enhanced crop protection and soil nutrient optimization, aligning with global food security imperatives. High-energy materials and aerospace sectors continue to rely on guanidine nitrate and related derivatives for controlled energetic compounds. Meanwhile, guanidine-based catalysts, resin modifiers, and flame retardants are gaining traction in advanced polymer systems, consumer electronics, and high-performance coatings.
Sustainability trends, including green urea routes, renewable ammonia, waste minimization, and cyanide-free synthesis pathways, are opening new investment areas for environmentally safer production technologies. Regionally, Asia Pacific remains the fastest-growing market; however, Europe and North America offer profitable entry points in pharma-grade guanidine, antimicrobial biguanides, and electronic-grade derivatives requiring stringent quality control. Strategic partnerships, co-located manufacturing hubs, and innovations in process safety and catalyst design will be pivotal in capturing long-term growth. For forward-looking stakeholders, these emerging hotspots represent pathways to differentiation, margin resilience, and leadership in a diversified yet essential chemical segment.
- Introduction (Product Definition, Taxonomy and Research Methodology)
- Executive Summary
- Guanidine Demand Supply Analysis
- Production by Country & Company
- Demand Supply Analysis
- Global Guanidine Market Assessment, 2020-2035
- Global Market Outlook (Value, Volume and Segmental Analysis)
- Regional Market Outlook (Value, Volume and Segmental Analysis)
- White Space & Emerging Investment Hotspot
- Market White Space Opportunities (Unmet demand, regional gaps, etc.)
- Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)
- Joint Ventures & Strategic Alliances
- Technology & Innovation Hotspots
- Regional Investment Attractiveness
- Barriers & Risks in Investment
- Guanidine Market Value Chain Analysis
- Raw Material Sourcing & Suppliers
- Key Raw Materials & Inputs (Ammonia, Urea, Calcium Carbide, Carbonate Salts)
- Supplier Landscape & Concentration (Country wise)
- Pricing Trends & Volatility
- Dependence on Imports vs Domestic Availability
- Distribution & Logistics
- Marketing & Sales Channels
- Value Addition & Profitability Across Chain
- Emerging Trends & Disruptions (high-purity biotech guanidine, pharma-grade shifts)
- Raw Material Sourcing & Suppliers
- Guanidine Market Pricing Analysis
- Historical Vs Projected Pricing Analysis (Global vs Regional Price Movements)
- Demand-Supply Impact on Prices
- Application-wise Pricing Differences
- Price Variation Across Key Countries
- Impact of Tariffs, Taxes, and Trade Policies
- Key Player Pricing Strategies
- Guanidine Technology Landscape
- Key Existing Technologies
- Overview of Mainstream / Commercially Adopted Technologies (Urea-based synthesis, ammonolysis routes)
- Advantages & Limitations
- Cost, Efficiency, and Scalability Aspects
- Emerging & Next-gen Technologies
- Pipeline & Under-development Technologies (biotech-grade purification, low-impurity guanidine derivatives)
- R&D Hotspots & Innovation Clusters
- Potential Disruption to Existing Methods
- Strategic Insights
- Future Technology Roadmap
- Opportunities for Differentiation via Technology
- Risks of Obsolescence & Barriers to Adoption
- Key Existing Technologies
- Policy & Regulatory landscape
- Competition Outlook (Leading 10 Companies)
- Competition Benchmarking
- Market Leaders Vs New Entrants
- Strategic Recommendations