- Overvew
- Table of Content
- Segmentation
- Segmentation
- Request Sample
Market Definition
Benzoic acid is an aromatic carboxylic acid primarily used as an intermediate in the production of a wide range of chemicals such as benzoate plasticizers, benzoyl chloride, alkyd resins, and preservatives. It naturally occurs in many plants and is synthetically produced via the partial oxidation of toluene. The market for benzoic acid has experienced considerable fluctuations in recent years due to changes in feedstock prices, evolving environmental regulations, and shifting demand dynamics across end-use industries such as food & beverage, pharmaceuticals, and personal care.
Market Insights
The benzoic acid market experienced moderate demand disruption in 2021 and 2022 due to raw material price volatility, particularly in toluene and benzene. However, market recovery began in 2023, supported by stable petrochemical supply and rising demand from downstream applications such as sodium benzoate and benzoate plasticizers. The forecast indicates steady growth, driven by increased consumption in food preservation, industrial coatings, and personal care products. Additional factors influencing demand include tightening regulatory norms on phthalate-based plasticizers, which have shifted focus toward benzoate derivatives as safer substitutes, and the growing emphasis on extending shelf life in packaged food products.
Environmental and regulatory trends in the EU are expected to shape long-term demand, especially with stricter restrictions on volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and the promotion of bio-based preservatives. Although the market is exposed to crude oil-linked price risks due to its reliance on toluene, overall global demand is projected to expand at a CAGR of 3.5% from 2023 to 2030. Asia-Pacific and Europe will remain key growth drivers due to expanding plasticizer and food additive industries.
The benzoic acid industry is moderately consolidated, with key multinational producers controlling most production capacity and exports. However, smaller regional manufacturers in China and India play a significant role in serving local markets and low-cost supply chains. The Russia-Ukraine conflict and related disruptions to petrochemical trade flows temporarily affected feedstock availability, though most producers have since diversified sourcing. Despite declining sales volumes during high feedstock price periods, overall revenues remained elevated due to strong price realizations.
Market Dynamics: Drivers
The key demand drivers for benzoic acid include the rising consumption of processed and packaged food, increased demand for safer non-phthalate plasticizers, and expanding usage in personal care formulations. Additionally, its growing role in pharmaceutical applications such as ointments, antifungal creams, and topical solutions supports market growth. The increasing push toward sustainable and low-toxicity preservatives also strengthens long-term prospects.
Market Dynamics: Challenges
The market faces challenges due to volatility in raw material costs (mainly toluene and benzene), stringent environmental regulations concerning synthetic preservatives, and the availability of bio-based alternatives such as sorbic acid. High dependency on petrochemical feedstocks also exposes producers to margin fluctuations. Furthermore, growing consumer preference for natural ingredients in food and cosmetics may gradually limit benzoic acid’s penetration in certain applications.
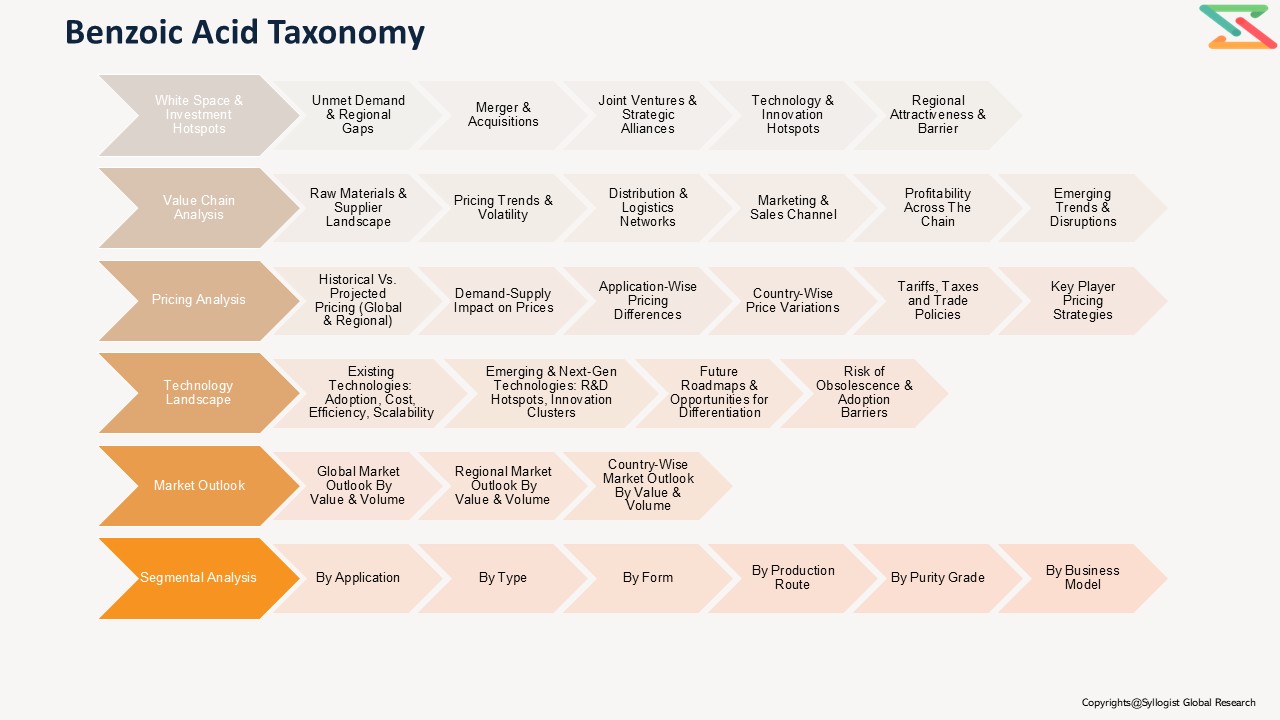
Market Segmentation
Based on Application, the Global Benzoic Acid Market is segmented into:
- Sodium Benzoate
- Potassium Benzoate
- Benzoate Plasticizers (DOP, DEHA substitutes)
- Benzoyl Chloride
- Alkyd Resins
- Others
Based on End-Use Industry, the Global Benzoic Acid Market is segmented into:
- Food & Beverages
- Chemical Intermediates
- Personal Care & Cosmetics
- Pharmaceuticals
- Industrial Coatings
- Others
Based on Source, the Global Benzoic Acid Market is segmented into:
- Petrochemical-based
- Bio-based
Based on Geography, the Global Benzoic Acid Market is segmented into:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
All market revenue has been given in US Dollar, while the market volumes are given in tons.
Historical Year: 2021–2024
Base Year: 2025
Estimated: 2026
Forecast: 2027–2031
Key Questions this Study will Answer
- What is the key overall market statistics or market estimates (Market Overview, Market Size, By Value, Market Size, By Volume, Forecast Numbers, Market Segmentation, Market Shares) of the Global Benzoic Acid Market?
- What is the region-wise industry size, growth drivers, challenges, and key market trends?
- What are the key innovations, opportunities, current and future trends, and regulations in the Global Benzoic Acid Market?
- Who are the key competitors, what are their strengths and weaknesses, and how do they perform in the Global Benzoic Acid Market based on competitive benchmarking matrix?
- What are the key insights derived from market surveys conducted during the Global Benzoic Acid Market study?
- Market Foundations & Dynamics
- Introduction
1.1. Product Overview (Definition & Scope of Benzoic Acid — technical, food, pharmaceutical grades; physical form)
1.1.2. Chemical Life-Cycle Overview (Feedstock → Synthesis → Purification → Derivatization → End-use → Disposal/Recycling)
1.1.3. Research Methodology
1.1.4. Executive Summary
1.1.5. Major Trends Shaping the Market (demand in preservatives, polymer additives, pharma; sustainability; feedstock dynamics)
1.1.6. Short-Term vs. Long-Term Opportunities (packaged food, personal care, polymer stabilizers vs. specialty derivatives)
1.1.7. Comparison of Production Routes (Toluene oxidation, Kolbe-Schmitt variants, bio-based routes)
1.1.8. Scenario Planning (Base, Optimistic, Conservative)
1.1.9. Sensitivity Analysis (feedstock/toluene price, regulatory changes, capacity additions)
1.1.10. Identification of Regional Investment Hotspots - Market Dynamics
- Introduction
- Drivers (growing processed food, rising cosmetic & pharma demand, polymer industry needs)
- Restraints (volatile aromatic feedstock prices, regulatory restrictions on preservatives in certain regions)
- Opportunities (bio-based benzoic acid, higher-purity pharma grades, downstream value-adds)
- Challenges (logistics of corrosive/acidic materials, competition from substitute preservatives)
- Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- Market Ecosystem & Value Chain
3.1. Overview of Value Chain Participants
1.3.1.1. Feedstock Suppliers (toluene, benzyl alcohol, raw aromatic producers)
1.3.1.2. Benzoic Acid Manufacturers (bulk & specialty producers)
1.3.1.3. Derivative Producers (sodium benzoate, benzoyl chloride, benzoic esters)
1.3.1.4. Formulators (food & beverage ingredient companies, cosmetics formulators, polymer additive blenders)
1.3.1.5. Distributors & Chemical Traders
1.3.1.6. End-Use Sectors (Food & Beverage, Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care, Plastics & Polymers, Chemicals)
1.3.2. Flow of Value and Material Through the Chain
1.3.3. Value Addition and Margins at Each Stage
1.3.3.1. Feedstock Procurement
1.3.3.2. Synthesis / Oxidation / Catalysis
1.3.3.3. Purification & Crystallization
1.3.3.4. Derivatization & Formulation
1.3.3.5. Distribution & Sales
1.3.4. Integration Trends (vertical integration of feedstock to downstream derivatives)
1.3.5. Impact of Vertical Integration on Cost & Supply Security - Mapping of Roles and Interdependencies
- Market Trends & Developments
5.1. White Market Space Analysis (bio-benzoic acid, specialty salts, high-purity pharma feedstock)
1.5.2. Demand–Supply Gaps (regional shortages, grade availability)
1.5.3. Investment Hotspots (manufacturing clusters, ports for aromatic feedstocks)
1.5.4. Unmet Needs (stable supply of pharma grade, greener process economics) - Risk Assessment Framework
6.1. Political / Geopolitical Risk (trade restrictions, sanctions on petrochemicals)
1.6.2. Operational Risk (process safety, emissions, plant shutdowns)
1.6.3. Environmental Risk (VOC, CO₂ footprint, effluent treatment)
1.6.4. Financial Risk (feedstock price swings, FX exposure)
- Market Ecosystem & Value Chain
- Regulatory Framework & Standards
- Global Regulatory Overview
1.1. Food Safety Regulations (EFSA, FDA limits & permitted uses for benzoic acid and sodium benzoate)
2.1.2. Pharmaceutical Monographs and Purity Standards (USP/Ph. Eur.)
2.1.3. Chemical Registration & Emissions (REACH, TSCA, China IECSC, India chemical rules)
2.2. Compliance & Certification Requirements (food grade certifications, GMP for pharma)
2.3. Transportation and Storage Regulations (hazard classification, packing group, UN codes)
2.4. Safety & Quality Standards (residual solvent limits, heavy metals, assay, impurities)
2.5. Environmental & Liability Considerations (waste streams, effluent, emissions control)
2.6. Traceability & Labeling Requirements (COA, country-specific labeling for food additives)
- Global Regulatory Overview
- Technology Landscape
- Production Technologies & Routes
1.1. Toluene Oxidation (catalysts, process variants)
3.1.2. Benzyl Alcohol Oxidation & Other Routes
3.1.3. Emerging Bio-based Production Routes (fermentation, biocatalysis)
3.2. Catalysts & Process Intensification (oxidation catalysts, continuous flow reactors)
3.3. Purification & Crystallization Technologies (filtration, drying, recrystallization for high purity)
3.4. Derivatization Processes (synthesis of sodium benzoate, benzoyl chloride, benzoate esters)
3.5. Quality Control & Analytical Methods (HPLC, GC, titration, ICP for trace metals)
3.6. Innovations to Reduce Energy & Emissions (heat integration, green oxidants)
3.7. Packaging & Stability Technologies
- Production Technologies & Routes
- Global, Regional & Country Forecasts (2020–2035)
- Global Benzoic Acid Market Outlook (value, volume)
- Market Share by:
2.1. By Application/End-Use (Food & Beverage preservatives, Sodium Benzoate production, Pharmaceuticals, Personal Care & Cosmetics, Polymer Additives/Plasticizers, Chemical Intermediates)
4.2.2. By Product Type (Benzoic Acid — technical, food grade, pharma grade; Sodium Benzoate; Benzoyl Derivatives)
4.2.3. By Form (Crystalline Powder, Granules, Solutions)
4.2.4. By Production Route (toluene oxidation, alternative, bio-based)
4.2.5. By Purity Grade (Industrial, Food, Pharma)
4.2.6. By Business Model (merchant supply, captive consumption, toll manufacturing)
4.2.7. By Company - Regional & Country Outlook (2020–2035)
3.1. Asia-Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, ASEAN)
4.3.2. North America (U.S., Canada, Mexico)
4.3.3. Europe (Germany, Netherlands, UK, France)
4.3.4. Latin America (Brazil, Argentina)
4.3.5. Middle East & Africa (UAE, South Africa)
- Pricing Analysis
- Overview of Pricing Structures (per kg / per ton; price by grade & form)
2. Average Selling Price (ASP) Trends by Grade, Application and Region
5.3. Cost Benchmark: Benzoic Acid vs. Substitute Preservatives & Intermediates
5.4. Price Sensitivity by Application (food vs. pharma vs. chemical intermediate)
5.5. Historical Price Evolution (2015–2025)
5.6. Forecast Pricing Curve (2025–2035)
5.7. Factors Influencing Price:
5.7.1. Toluene & Aromatics Feedstock Price
5.7.2. Energy, Utilities & Catalysts
5.7.3. Purification & Compliance Costs
5.8. Regional Pricing Differentiation (Asia vs. Europe vs. North America)
5.9. Impact of Bio-based Route Commercialization on Pricing
- Overview of Pricing Structures (per kg / per ton; price by grade & form)
- Competition Outlook
- Market Concentration and Fragmentation Level
2. Company Market Shares (Top 10 Players — global & regional)
6.3. Competitive Strategies (capacity expansions, backward integration, specialty grades)
6.4. Benchmarking Matrix (Scale vs. Purity Portfolio vs. Geographic Reach)
6.5. Recent Developments (M&A, capacity projects, joint ventures, new green processes)
- Market Concentration and Fragmentation Level
- Cost Structure & Margin Analysis
- Detailed Cost Breakdown (feedstock, catalysts, utilities, labor, effluent treatment)
2. Average Cost per Stage (synthesis, purification, derivatization, packaging)
7.3. Profitability and Margin Distribution Along Value Chain
7.3.1. Feedstock Supplier Margin
7.3.2. Benzoic Acid Manufacturer Margin
7.3.3. Downstream Derivatives / Formulator Margin (e.g., sodium benzoate processors)
7.3.4. Distributor / Trader Margin
7.4. Sensitivity Analysis: How Feedstock Prices & Purity Requirements Impact Margin
7.5. Cost Reduction Opportunities (process optimization, co-location with aromatic producers, continuous processes)
- Detailed Cost Breakdown (feedstock, catalysts, utilities, labor, effluent treatment)
- Business Models & Strategic Insights
- Merchant Commodity Supplier Models
2. Integrated Manufacturer Models (feedstock → benzoic acid → derivatives)
8.3. Toll Manufacturing & Contract Production Models
8.4. Specialty / High-Purity Producer Models (pharma, high-end personal care)
8.5. Value-Added Formulation & Branding Models (preservative blends, consumer ingredient packs)
8.6. Economic Viability Comparison of Models
8.7. SWOT Analysis of Leading Models
- Merchant Commodity Supplier Models
- Investment & Financial Analysis
- CAPEX and OPEX Benchmarks for Benzoic Acid Plants (small, medium, large scale)
2. Payback Period and IRR Sensitivity (by region & product mix)
9.3. Financial Modeling Assumptions (capacity utilisation, yield, price realizations)
9.4. Revenue Streams: Bulk Sales, Premium Grade Sales, Derivative Sales (sodium benzoate, esters)
9.5. Investment Case Studies (greenfield plant, backward integration with aromatic feedstock, conversion to bio-route)
9.6. Funding Landscape: Strategic Investors, Private Equity, Green Financing
- CAPEX and OPEX Benchmarks for Benzoic Acid Plants (small, medium, large scale)
- Sales & Distribution Channel Analysis
- Overview of Go-to-Market Channels
1.1. Direct Sales (manufacturer → large end-user e.g., food ingredient companies)
10.1.2. Indirect Sales via Distributors & Chemical Traders
10.1.3. Toll & Contract Manufacturing Arrangements
10.2. Channel Share by Region
10.3. Typical Channel Flow Diagram (manufacturer → distributor → formulator → end-user)
10.4. Sales Process (specification, sampling, certification, QC, logistics)
10.5. Distribution Strategies by Leading Players (local warehousing, multi-modal logistics)
10.6. Emerging Trends:
10.6.1. Direct B2B Ingredient Marketplaces
10.6.2. On-demand Toll Manufacturing Platforms
10.6.3. Traceability & Digital Certificates of Analysis
- Overview of Go-to-Market Channels
- Strategic Recommendations & Roadmap
- Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives (sustainability claims, capacity diversification)
2. Future Outlook (next 5–10 years — bio-routes, regulatory tightening, premiumization)
11.3. Strategic Recommendations
11.3.1. Technology & Process Advancements to Watch (continuous oxidation, greener oxidants, biocatalysis)
11.3.2. Circularity & Feedstock Security Roadmap (2030–2035)
11.3.3. Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders (manufacturers, formulators, investors)
11.4. Benzoic Acid Market Acceleration Roadmap
11.4.1. Short-term (2025–2027): Strengthen QA/QC for food & pharma grades, secure feedstock supply
11.4.2. Mid-term (2028–2030): Scale specialty grades and downstream integration, pilot bio-routes
11.4.3. Long-term (2031–2035): Commercial bio-benzoic acid, low-emission production, higher margin specialty penetration
11.5. Tailored recommendations for:
11.5.1. Benzoic Acid Manufacturers
11.5.2. Derivative & Formulator Companies (sodium benzoate, esters)
11.5.3. End Users (food manufacturers, pharma, personal care brands)
11.6. Recommendations on Key Success Factors
11.6.1. Strategic Partnerships & Alliances (feedstock, offtake, R&D)
11.6.2. Digitalization & Quality Traceability (COA platforms, batch tracking)
11.6.3. Regulatory Alignment & Certification Compliance (food & pharma approvals)
11.6.4. Investor Confidence & Capital Availability
- Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives (sustainability claims, capacity diversification)