- Overvew
- Table of Content
- Segmentation
- Segmentation
- Request Sample
Global Formaldehyde Market: Foundation Chemical Powering Multi-Sector Growth
Driving Industrial Transformation Through Material Innovation
The global formaldehyde market is undergoing a period of strategic evolution, driven by advances in production technologies, heightened regulatory scrutiny, and expanding demand from value-added downstream derivatives. As one of the most versatile building-block chemicals, formaldehyde plays a central role in engineered wood resins, thermoset plastics, coatings, agrochemicals, automotive components, and textile treatments. The industry is witnessing notable shifts toward low-emission, ultra-low VOC resins, driven by tighter environmental standards (CARB, EPA, REACH) and growing customer preference for sustainable, performance-enhanced materials. Innovations in catalytic oxidation, methanol efficiency improvement, continuous production systems, and emission-controlled reactors are improving yields, reducing energy consumption, and lowering environmental footprints. At the same time, the push toward bio-methanol and circular carbon sources is positioning formaldehyde producers for future decarbonization pathways. Collectively, these technological advancements reflect a structural modernization of the formaldehyde ecosystem and reinforce its importance as a critical intermediate for global manufacturing and construction.
Mapping the Value Chain: From Methanol Feedstock to High-Value Derivatives
The formaldehyde value chain is highly interconnected, with upstream methanol availability and pricing playing the dominant role in determining production economics. Formaldehyde is predominantly produced via silver-catalyst or metal-oxide processes, where feedstock efficiency, catalyst life, and plant configuration significantly impact cost structures. Midstream, large-scale producers convert formaldehyde into a variety of downstream derivatives including urea formaldehyde (UF), phenol formaldehyde (PF), melamine formaldehyde (MF), pentaerythritol, 1,4-butanediol (BDO), hexamine, and paraformaldehyde. These intermediates ultimately feed into industries such as engineered wood, laminates, automotive components, insulation foams, agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and industrial resins. Downstream, demand is shaped by construction cycles, furniture production, automotive manufacturing, and regulatory requirements for emission control in composite wood products. Stringent compliance norms, especially in North America and Europe, have reshaped procurement practices, encouraging manufacturers to develop E0, E1, and ultra-low emitting resin systems. Increasingly, producers are pursuing backward integration into methanol and forward integration into resin systems to stabilize margins, improve supply security, and deepen relationships with OEMs, panel manufacturers, and adhesive formulators.
Balancing Global Demand and Supply Dynamics
Demand for formaldehyde and its derivatives remains structurally strong, closely aligned with macro indicators such as housing construction, furniture production, and industrial resin consumption. Asia Pacific continues to dominate global demand, led by China’s expansive engineered wood industry, rapid urbanization, and superior cost economics. North America and Europe are experiencing more measured growth but with rising penetration of low-emission wood panels and higher-value specialty resins. On the supply side, new capacities are concentrated in Asia, the Middle East, and parts of Eastern Europe, driven by proximity to methanol hubs and cost-competitive energy markets. However, the industry continues to face challenges including volatile methanol prices, environmental compliance costs, operational risks in continuous plants, and tightening regulations on formaldehyde emissions in indoor air environments. Additionally, any disruptions in methanol supply, stemming from geopolitical uncertainties, gas feedstock shortages, or plant shutdowns, can immediately cascade into the formaldehyde and resin value chain. These structural dynamics highlight the need for strategic raw material planning, advanced process control, and regional diversification to maintain balanced supply-demand alignment.
Pricing Dynamics: Managing Volatility in a Feedstock-Driven Market
Pricing in the formaldehyde sector is primarily driven by methanol cost fluctuations, plant utilization rates, transportation logistics, and regulatory compliance investments. Given methanol’s significant share in production cost, formaldehyde prices often move closely in tandem with crude oil and natural gas trends. Regions with lower methanol production costs, such as the Middle East and parts of China, maintain competitive advantages, while North America and Europe typically exhibit pricing premiums, reflecting higher compliance, energy, and transportation costs. Specialty grades such as high-purity paraformaldehyde, stabilized formaldehyde solutions, and derivative products (UF/PF/MF resins, hexamine, pentaerythritol) command differentiated pricing based on application criticality, molecular stability, and tailored performance characteristics. Market volatility also stems from regulatory transitions introducing strict indoor air-quality standards, prompting resin manufacturers to redesign formulations and invest in advanced emission-control technologies. As the market evolves, pricing is increasingly influenced not only by feedstock costs but also by value-delivery factors such as product consistency, emission ratings, certification compliance, and lifecycle cost benefits.
White Space and Emerging Investment Hotspots
Several emerging opportunities are reshaping the formaldehyde investment landscape. Sustainability is the most significant driver, with strong momentum toward bio-methanol integration, carbon-neutral resin systems, and recyclable engineered wood products. The transition to ultra-low and no-added-formaldehyde (NAF) resins is opening new avenues for innovation in construction adhesives and eco-friendly furniture manufacturing. Growth in electric mobility and lightweight automotive materials is expanding use cases for formaldehyde-based polyols, composites, and high-performance resins. Rapid expansion in packaging, insulation materials, binders for mineral wool, and agricultural chemicals is also generating new downstream demand. Regionally, Asia Pacific remains the fastest-expanding marketplace; however, North America and Europe offer high-value opportunities in specialty derivatives, compliant panel products, and next-generation binder technologies. Strategic partnerships, R&D investments in resin chemistry, and regional manufacturing hubs closer to methanol-rich economies are expected to unlock long-term competitive advantages. For forward-looking players, these white spaces represent pathways to sustainable growth, differentiation, and improved margin resilience in a maturing but essential chemical market.
- Introduction (Product Definition, Taxonomy and Research Methodology)
- Executive Summary
- Formaldehyde Demand Supply Analysis
- Production by Country & Company
- Demand Supply Analysis
- Global Formaldehyde Market Assessment, 2020-2035
- Global Market Outlook (Value, Volume and Segmental Analysis)
- Regional Market Outlook (Value, Volume and Segmental Analysis)
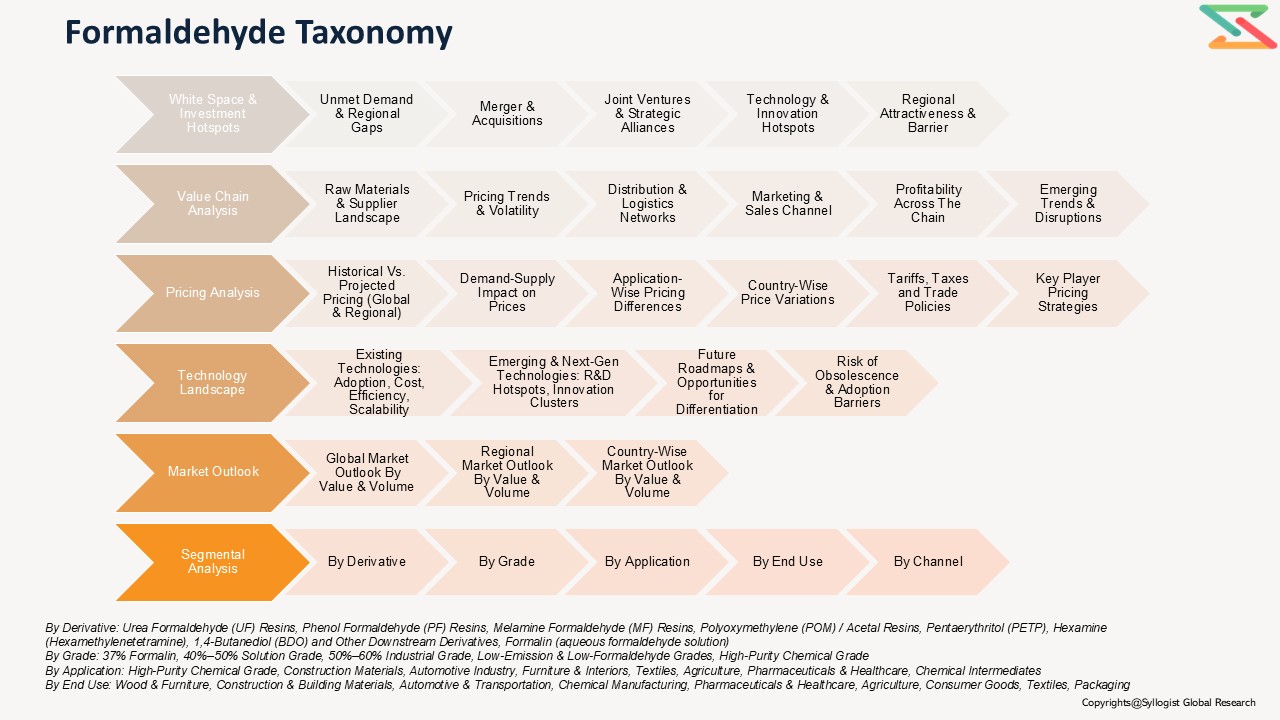
- White Space & Emerging Investment Hotspot
- Market White Space Opportunities (Unmet demand, regional gaps, etc.)
- Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)
- Joint Ventures & Strategic Alliances
- Technology & Innovation Hotspots
- Regional Investment Attractiveness
- Barriers & Risks in Investment
- Formaldehyde Market Value Chain Analysis
- Raw Material Sourcing & Suppliers
- Key Raw Materials & Inputs (Methanol, Catalysts, Utilities)
- Supplier Landscape & Concentration (Country wise)
- Pricing Trends & Volatility
- Dependence on Imports vs Domestic Availability
- Distribution & Logistics
- Marketing & Sales Channels
- Value Addition & Profitability Across Chain
- Emerging Trends & Disruptions (low-emission resins, sustainable binders)
- Raw Material Sourcing & Suppliers
- Formaldehyde Market Pricing Analysis
- Historical Vs Projected Pricing Analysis (Global vs Regional Price Movements)
- Demand-Supply Impact on Prices
- Application-wise Pricing Differences
- Price Variation Across Key Countries
- Impact of Tariffs, Taxes, and Trade Policies
- Key Player Pricing Strategies
- Formaldehyde Technology Landscape
- Key Existing Technologies
- Overview of Mainstream / Commercially Adopted Technologies (Silver Catalyst Process, Iron-Molybdenum Catalyst Process)
- Advantages & Limitations
- Cost, Efficiency, and Scalability Aspects
- Emerging & Next-gen Technologies
- Pipeline & Under-development Technologies (low-VOC binders, formaldehyde-free resin systems)
- R&D Hotspots & Innovation Clusters
- Potential Disruption to Existing Methods
- Strategic Insights
- Future Technology Roadmap
- Opportunities for Differentiation via Technology
- Risks of Obsolescence & Barriers to Adoption
- Key Existing Technologies
- Policy & Regulatory landscape
- Competition Outlook (Leading 10 Companies)
- Competition Benchmarking
- Market Leaders Vs New Entrants
- Strategic Recommendations