- Overvew
- Table of Content
- Segmentation
- Request Sample
Market Definition
Second-life batteries refer to used electric vehicle (EV) batteries that are repurposed and redeployed for applications beyond their initial automotive use. Once EV batteries degrade to about 70–80% of their original capacity, they become unsuitable for vehicle propulsion but still retain significant energy storage potential. These batteries are refurbished, tested, and integrated into stationary or secondary applications such as residential, commercial, utility-scale energy storage, and EV charging infrastructure.
Unlike recycling, which focuses on material recovery, second-life utilization extends the functional lifespan of lithium-ion and other chemistries through reuse. This process involves diagnostics, grading, repackaging, and reassembly of battery modules or packs. The approach reduces both battery waste and lifecycle carbon footprint, making it a crucial element in the circular economy of electric mobility.
Major chemistries suitable for second-life applications include Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC), Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA), Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH), and Lead-acid, with emerging interest in hybrid multi-chemistry systems for optimized performance.
Market Insights
The Global Second-Life Battery Market is experiencing significant growth momentum, expected to rise from USD 683 million in 2022 to around USD 13,652 million by 2035, registering a robust CAGR of 23% during 2025–2035. This expansion is primarily driven by the increasing penetration of electric vehicles (EVs), the scaling of renewable energy storage requirements, and growing global emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles. As EV adoption accelerates, a rising number of batteries are reaching their end-of-first-life, creating a substantial pool of usable storage assets. Governments and industries are increasingly recognizing second-life batteries as a cost-efficient and environmentally sustainable solution to manage energy storage needs, particularly in residential and commercial applications.
From a chemistry standpoint, Hybrid Second-Life Systems, which integrate multiple chemistries and reuse configurations, are expected to dominate the market, growing at a CAGR of over 35–40% between 2025 and 2035. These systems offer high flexibility and adaptability, making them suitable for both distributed energy storage and grid-scale installations. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries follow closely, propelled by their superior thermal stability, long cycle life, and increasing use in EV manufacturing, particularly in China and other Asia-Pacific countries. These characteristics position LFP as the most commercially viable chemistry for second-life deployment.
Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) and Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA) chemistries are projected to maintain steady adoption at 25–30% CAGR, favored for their high energy density and strong suitability for commercial and industrial (C&I) applications where performance requirements are stringent. On the other hand, Lead-acid and Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) batteries are expected to occupy niche roles in specific segments such as telecom backup and remote off-grid installations, offering lower growth potential due to limited scalability and technological obsolescence.
In terms of applications, the Residential Energy Storage segment is projected to grow the fastest, with a CAGR of around 30–32%, supported by the rapid adoption of rooftop solar systems and growing prosumer participation in decentralized energy systems. The Commercial & Industrial (C&I) Energy Storage segment, which accounted for the largest share in 2024, will continue to expand at a strong 25–28% CAGR, driven by demand for peak shaving, load management, and microgrid stability in commercial buildings and manufacturing facilities.
EV Charging Stations (Load Balancing) represent another fast-emerging opportunity, growing at approximately 25% CAGR, as second-life batteries are increasingly utilized to buffer grid loads and reduce electricity costs during peak demand periods. The Utility-Scale Energy Storage segment is expected to grow moderately at 15–18% CAGR, with adoption constrained by safety regulations, limited warranties, and performance concerns surrounding repurposed batteries. Meanwhile, Power Backup/UPS systems—particularly in telecom and remote infrastructure—are expected to maintain a stable but smaller market share, expanding at roughly 15% CAGR due to sustained demand in developing regions.
A comparative bubble analysis indicates that C&I and residential storage systems represent the most commercially attractive and high-growth opportunities, while utility-scale deployment remains relatively slower. Regionally, Asia-Pacific and Europe are leading the global market, supported by favorable policy frameworks promoting EV battery reuse and recycling mandates. North America follows closely, with growing activity in community-scale and residential energy storage projects, reflecting increased participation from utilities and technology providers.
Market Dynamics: Drivers
The first major driver of the second-life battery market is the surge in EV adoption and the resulting influx of retiring battery volumes. By 2030, over 11 million metric tons of EV batteries are expected to reach end-of-first-life, creating a substantial supply for reuse. Leading OEMs are partnering with energy developers and utilities to establish structured repurposing programs, capturing value before recycling.
Secondly, circular economy and sustainability commitments are pushing governments and corporations toward reuse models that minimize waste and carbon emissions. Extending battery life through second-life use can cut lifecycle emissions by up to 50% compared to new battery manufacturing or direct recycling. This approach aligns with global regulatory initiatives such as the EU Battery Regulation (2023) and China’s Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework, both of which prioritize reuse over recycling.
Thirdly, the economic viability of reuse models is becoming increasingly evident. Second-life batteries are typically 30–70% cheaper than new ones, providing attractive economics for residential, commercial, and grid storage systems. These cost advantages, combined with growing energy price volatility, are driving interest from industrial users and energy service companies seeking to maximize ROI.
Lastly, technological advancements in diagnostics and monitoring are transforming the second-life value chain. The use of AI-based state-of-health (SOH) assessment, digital twins, and automated grading systems has improved testing precision, safety, and refurbishment scalability. This has enabled OEMs, independent refurbishers, and utilities to develop standardized processes for integrating repurposed batteries into energy storage applications.
Market Dynamics: Challenges
Despite its promising outlook, the market faces several challenges. The foremost issue is the lack of standardization and safety protocols. There are no universally accepted standards for testing, labeling, or certifying second-life batteries, resulting in inconsistency in quality and safety across suppliers. Variability in battery condition and configuration complicates system design and raises insurance and regulatory concerns.
Another major challenge is limited access to OEM data, particularly from proprietary Battery Management Systems (BMS). Independent refurbishers often lack detailed usage histories or performance records, making accurate state-of-health evaluation complex and costly.
The uncertainty around residual value and warranty coverage also hampers large-scale adoption. Without standardized warranties or predictable performance guarantees, institutional investors and utilities remain cautious about deploying second-life systems for long-duration grid applications.
Finally, the market faces competition from advanced recycling technologies. As recycling efficiency improves and raw material recovery becomes more economically attractive, recyclers increasingly compete with refurbishers for end-of-life batteries, potentially constraining feedstock availability for reuse applications.
Overall, while the second-life battery market presents enormous economic and environmental potential, overcoming these standardization, data-sharing, and policy challenges will be critical to unlocking its full value over the next decade.
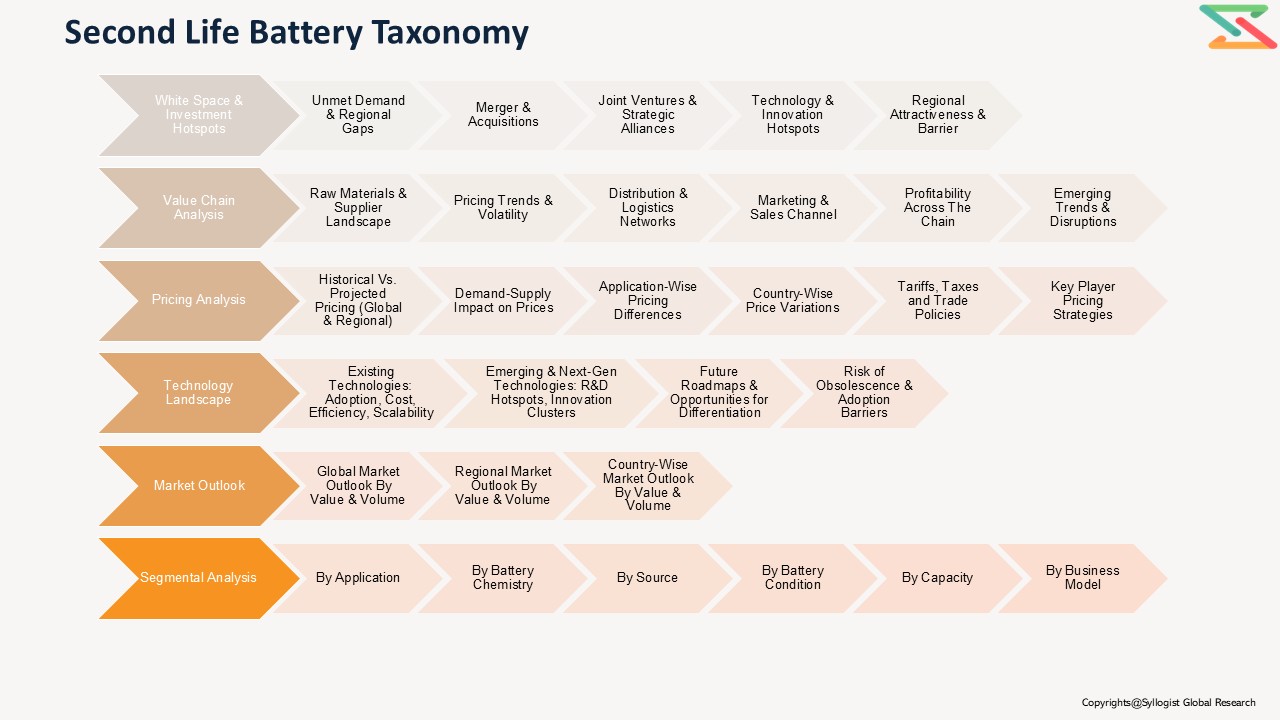
Market Segmentation
- Based on Battery Chemistry, the Global Second Life Battery market is segmented into
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP)
- Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC)
- Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA)
- Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH)
- Lead-acid
- Hybrid Second-Life Systems
- Based on Application, the Global Second Life Battery market is segmented into
- Utility-Scale Energy Storage
- Commercial & Industrial (C&I) Energy Storage
- Residential Energy Storage
- EV Charging Stations (Load Balancing)
- Power Backup / UPS (Telecom, Remote Infrastructure)
- Based on Business Model, the Global Second Life Battery market is segmented into
- OEM-Owned Circular Models
- Independent Refurbisher Models
- Battery Leasing / Subscription Models
- Integrated Reuse + Recycling Models
- Utility & Solar Developer Partnerships
- Based on Battery Condition, the Global Second Life Battery market is segmented into
- Used Batteries
- Refurbished Batteries
- Recycled Batteries
- Based on Source, the Global Second Life Battery market is segmented into
- Electric Cars
- Electric Buses
- Two-Wheelers
- Other Electric Vehicles
- Based on Capacity, the Global Second Life Battery market is segmented into
- <10 kWh
- 10–100 kWh
- 100 kWh–1 MWh
- >1 MWh
- Based on Geography, the Global Second Life Battery market is segmented into
- Asia-Pacific
- North America
- Europe
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
- All market revenue has been given in US Dollar, while the market volumes are given in million tons.
Historical Year: 2020-2024
Base Year: 2025
Estimated: 2026
Forecast- 2027-2035
Key Questions this Study will Answer
- What are the key overall market statistics or market estimates (Market Overview, Market Size- By Value, Market Size-By Volume, Forecast Numbers, Market Segmentation, Market Shares) of Global Second Life Battery Market?
- What is the region wise industry size, growth drivers and challenges key market trends?
- What are the key innovations, opportunities, current and future trends and regulations in the Global Second Life Battery Market?
- Who are the key competitors, what are their key strength and weakness and how they perform in Global Second Life Battery Market based on competitive benchmarking matrix?
- What are the key results derived from the market surveys conducted during Global Second Life Battery Market study?
- Market Foundations & Dynamics
- Introduction
- Product Overview (Definition & Scope of Second-Life Batteries)
- Battery Life-Cycle Overview (First Life → Second Life → Recycling)
- Research Methodology
- Executive Summary
- Major Trends Shaping the Market
- Short-Term vs. Long-Term Opportunities
- Comparison of Reuse vs. Recycling Pathways
- Scenario Planning (Base, Optimistic, Conservative)
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Identification of regional investment hotspots
- Market Dynamics (Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, PESTLE Analysis)
- Market Ecosystem & Value Chain
- Overview of Value Chain Participants
- EV OEMs and Battery Manufacturers
- Collection & Logistics Companies
- Diagnostic and Grading Firms
- Repackaging / Refurbishment Facilities
- Energy Storage Integrators / EPCs
- End-Use Sectors
- Raw Material Suppliers (leading, mid-size and start-ups suppliers Profile)
- Flow of Value and Material Through the Chain
- Value Addition and Margins at Each Stage
- Collection
- Testing/Diagnostics
- Repackaging
- System Integration
- Distribution/Sales
- Integration Trends (OEM-Controlled vs. Independent Models)
- Impact of Vertical Integration
- Overview of Value Chain Participants
- Mapping of roles and interdependencies
- Market Trends & Developments
- White Market Space Analysis
- Demand–Supply Gaps
- Investment Hotspots
- Unmet Needs
- Risk Assessment Framework
- Political/geopolitical risk
- Operational risk
- Environmental risk
- Financial risk
- Introduction
- Regulatory Framework & Standards
- Global Regulatory Overview
- EU Battery Regulation (2023/2024 update)
- S. EPA & DOE Circular Battery Guidelines
- China’s Reuse & Recycling Policy
- India’s Battery Waste Management Rules
- Compliance & Certification Requirements
- Transportation and Storage Regulations (ADR, UN38.3)
- Safety & Quality Standards
- Environmental & Liability Considerations
- Battery Passport Initiatives & Digital Traceability
- Global Regulatory Overview
- Technology Landscape
- Diagnostic & Grading Technologies
- EIS, Machine Learning SOH Estimation, Automated Sorting
- Repackaging & Refurbishment Techniques
- BMS Adaptation and Integration Challenges
- Standardization & Modular Design Trends
- Future Outlook: Solid-State & Hybrid Chemistries
- Innovations to Reduce Testing & Reuse Cost
- Diagnostic & Grading Technologies
- Global, Regional & Country Forecasts (2020–2035)
- Global Second Life Battery Market Outlook (value, volume)
- Market Share by
- Application/End-Use (Utility-Scale Energy Storage, Commercial & Industrial (C&I) Energy Storage, Residential Energy Storage, EV Charging Stations, Power Backup/Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS))
- Battery Chemistry (Lithium-ion Batteries (Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC), Nickel Cobalt Aluminum (NCA), Lead-Acid Batteries, Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries, Hybrid Second-Life Systems)
- Battery Condition (Used Batteries, Refurbished Batteries, Recycled Batteries)
- Source (Electric Cars, Electric Buses, Two-Wheelers, Other Electric Vehicles)
- Capacity (<10 kWh, 10–100 kWh, 100 kWh–1 MWh, >1 MWh)
- Business Model (OEM Reuse Program, Independent Repurposers, Leasing / Subscription Models, Integrated Circular Model, Utility / EPC Partnerships)
- Company
- Regional & Country Outlook (2020-2035)
- Asia-Pacific (China, Japan, South Korea, India, Australia)
- North America (US, Canada)
- Latin America (Brazil, Mexico)
- Europe (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Spain)
- Middle East & Africa (UAE, Saudi Arabia, South Africa)
- Pricing Analysis
- Overview of Pricing Structures (per kWh basis)
- Average Selling Price (ASP) Trends by Battery Type and Region
- Cost Benchmark:
- New Li-ion Battery vs. Second-Life Battery
- ESS Installed Cost Comparison ($/kWh)
- Price Sensitivity by Application
- C&I, Residential, Telecom, Utility
- Historical Price Evolution (2015–2025)
- Forecast Pricing Curve (2025–2035)
- Factors Influencing Price:
- Testing & Repackaging Cost
- Logistics & Collection
- Warranty / Insurance Overhead
- Safety Certification & Compliance Cost
- Regional Pricing Differentiation (China vs. EU vs. U.S.)
- Impact of New Battery Cost Decline on SLB Pricing
- Competition Outlook
- Market Concentration and Fragmentation Level
- Company Market Shares (Top 10 Players)
- Competitive Strategies
- OEM-Led Reuse Programs
- Independent Integrator Approaches
- Joint Ventures (OEM + Utility)
- Benchmarking Matrix (Business Model vs. Scale vs. Integration)
- Recent Developments
- Partnerships, M&A, Funding, and Capacity Expansions
- Cost Structure & Margin Analysis
- Detailed Cost Breakdown
- Procurement (used pack purchase)
- Disassembly / Diagnostics
- Reconfiguration / BMS Integration
- Packaging & Testing
- BOS Components (Inverter, Cooling, Enclosure)
- Labor & Certification
- Average Cost per Stage (in $/kWh)
- Profitability and Margin Distribution Along Value Chain
- OEM Margin
- Repurposer / Refurbisher Margin
- System Integrator Margin
- Distributor Margin
- Sensitivity Analysis: How Price & SOH Impact Margin
- Cost Reduction Opportunities via Automation & AI Diagnostics
- Detailed Cost Breakdown
- Business Models & Strategic Insights
- OEM-Owned Circular Models
- Independent Refurbisher Models
- Battery Leasing / Subscription Models
- Integrated Reuse + Recycling Business Models
- Partnerships with Utilities / Solar Developers
- Economic Viability Comparison of Models
- SWOT Analysis of Leading Models
- Investment & Financial Analysis
- CAPEX and OPEX Benchmarks for SLB Systems
- Payback Period and IRR Sensitivity (by Application)
- Financial Modeling Assumptions (SOH, Cycle Life, Degradation)
- Revenue Streams:
- Energy Arbitrage
- Peak Shaving
- Capacity Payments
- Carbon Credits / Circular Incentives
- Investment Case Studies
- Funding Landscape: Venture Capital & Strategic Investments
- Sales & Distribution Channel Analysis
- Overview of Go-to-Market Channels
- Direct Sales (OEM to End-User)
- Indirect Sales via Integrators / EPCs
- Partnership Models (OEM + Utility, OEM + Start-up)
- Online Platforms for Used Battery Trading
- Channel Share by Region
- Typical Channel Flow Diagram
- Sales Process (Procurement → Repurposing → Deployment → O&M)
- Distribution Strategies by Leading Players
- Emerging Trends:
- Battery-as-a-Service (BaaS)
- Subscription or Leasing Models
- Platformization / Battery Marketplace Startups
- Overview of Go-to-Market Channels
- Strategic Recommendations & Roadmap
- Competitors’ Strategic Initiatives
- Future Outlook (next 5–10 years, emerging players, success factors)
- Strategic Recommendations
- Technology Advancements to Watch
- Circular Economy Integration Roadmap (2030–2035)
- Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
- Second Life Battery Market Acceleration Roadmap
- Short-term (2025–2027)
- Mid-term (2028–2030)
- Long-term (2031–2035)
- Tailored recommendations for:
- For Second Life Battery Manufacturers
- For Raw Material Manufacturers
- For End Users
- Recommendations on Key Success Factors
- Partnerships & Alliances
- Digitalization & AI Integration
- Policy Alignment & Certification Compliance
- Investor Confidence & Capital Availability
- Market Foundations & Dynamics